The Unsung Heroes: How Non-Revenue Generating Roles Support Revenue-Generating Roles
In an economy like we are facing today, the support provided by non-revenue generating jobs to revenue-generating jobs becomes even more critical. Economic downturns often lead to budget cuts, reduced consumer spending, and increased competition, making it essential for companies to operate with heightened efficiency and strategic focus. This article will identify the difference between non-revenue generating and revenue-generating jobs and explain the importance of non-revenue generating jobs to an organization’s success.
Revenue-Generating Roles Vs Non-Revenue Generating Roles
Revenue-Generating Roles are positions that directly contribute to an organization’s income. Examples of these roles include:
- Sales Representatives: These professionals are tasked with identifying prospective customers, nurturing client relationships, and closing deals to generate revenue for the organization.
- Marketing Managers: These individuals devise strategic campaigns, conduct market research, and oversee promotional activities to enhance brand visibility and drive sales.
- Account Executives: Their role involves identifying growth opportunities, forging partnerships, and expanding the organization’s market reach to drive revenue growth.
Non-Revenue Generating Roles do not directly add to a company’s income but are vital to create an environment where revenue-generating jobs can thrive. Examples of roles in this sector include:
- Human Resources: HR departments play a pivotal role in recruiting, training, and retaining talent. Effective HR practices ensure that the company attracts skilled professionals for both revenue and non-revenue generating roles. HR professionals handle employee benefits, conflict resolution, and compliance with labor laws, creating a stable and compliant work environment. This support enables sales teams and other revenue generators to focus on their primary tasks without being bogged down by administrative or legal issues.
- Information Technology: IT professionals maintain the technological infrastructure, ensuring that a company’s systems are secure, efficient, and up-to-date. They handle everything from routine maintenance to troubleshooting critical issues. A robust IT support system ensures that the sales and marketing (revenue-generating) teams can rely on their customer relationship management systems, communication tools, and data analytics platforms by enhancing their productivity and efficiency. This function can ultimately save the company hundreds of thousands of dollars, in turn ensuring revenue generation is functioning at its optimum levels.
- Administrative Assistants: These individuals manage schedules, coordinate meetings, and handle communication tasks, allowing revenue-generating staff to focus on client interactions and strategic initiatives. By taking care of logistical details, administrative assistants enhance the productivity of sales teams and executives, ensuring that they can devote more time to revenue-generating activities.
- Facility Management: These teams are responsible for maintaining a safe, clean, and functional workplace. This includes everything from office maintenance to managing supplies and ensuring compliance with health and safety regulations. A well-maintained work environment boosts employee morale and productivity, directly impacting the efficiency of revenue-generating teams.
- Compliance and Legal: These professionals ensure that the company adheres to local and international laws and regulations. They mitigate risks by managing legal documentation, contracts, and regulatory filings. This vigilance prevents costly legal issues and allows for revenue-generating teams to operate within a secure and compliant framework.
- Finance and Accounting: Employees in these departments manage the company’s finances, from budgeting and forecasting to payroll and financial reporting. Accurate financial management is crucial for making informed business decisions, securing investments, and ensuring cash flow. This financial stability is foundational for sales and business development teams, who rely on timely financial information to strategize and execute revenue-generating activities.
- Research and Development (R&D): These professionals drive innovation by developing new products and improving existing ones. While their contributions may not immediately translate into revenue, they lay the groundwork for future growth. Revenue-generating teams depend on the innovations and advancements from R&D to offer competitive products and services in the market.
- Customer Support: These individuals handle inquiries, troubleshoot problems, and assist clients. They foster customer loyalty and retention by ensuring customer satisfaction and addressing issues promptly. Happy customers are more likely to make repeat purchases and recommend the company to others, indirectly contributing to revenue generation.
Non-revenue generating roles constitute a large portion of what keeps a company running by supporting the revenue-generating roles and ensuring smooth business operations. They even represent most of the workforce as illustrated in the below graph (One Model):
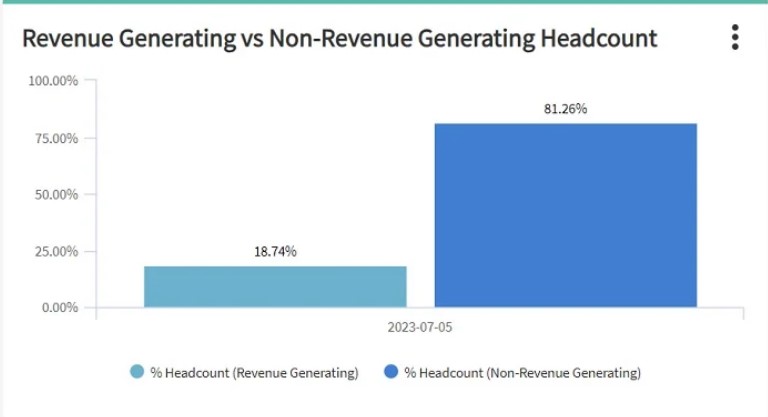
Non-revenue generating roles support other departments by offering consulting, training, and tools or systems to make others more efficient.
An Organizational Scenario
Think about a financial services company that makes its revenue from selling different products and services. There is a huge need for sales representatives, field consultants, advisors and the like to provide customers with solutions to purchase to meet their financial needs. However, how can the individuals in these positions act in a revenue-generating capacity? Human Resources is needed to search and screen potential candidates. Training personnel are needed to educate individuals on the products and services they will be selling. Information Technology is needed to provide the technical support to conduct business and complete training. Finance and Accounting are needed to ensure budgets are in line, people are paid correctly, and on time. Research and Development continue idea generating for the next big offer, or learns more about how to offer current products and services in a more cost-friendly manner with better benefits. There is a need to provide good support for customers with questions or concerns. Without these non-revenue generating positions, business as we know it would come to a screeching halt for each organization.
Delegating Non-Revenue Generating Tasks
Many times, leaders in organizations try to delegate the responsibilities of some non-revenue generating staff to other individuals. This strategy, more often than not, can actually reduce a company’s bottom line. For example, an Executive Director making $70,000 annually equates to $33.65 hourly. If that individual spends ten hours a week on non-revenue generating tasks, these tasks cost the company almost $18,000 per year. This begs the question of whether the Executive Director can use those hours each week to raise the company’s revenue by $18,000 annually. If the answer is yes, then the organization should look to delegate that work to non-revenue generating roles (Forbes).
The experienced non-revenue generating employees can do the job more quickly, and at a higher quality, than someone without that knowledge. Causing employees to take on too much responsibility can cause their performance to suffer in other areas, like generating revenue for the company, because they have to spend extra time doing work they aren’t familiar with. This can also make an organization stray from its intended mission and vision, and as a result, lose customer loyalty and trust (Forbes).
Final Remarks
Non-revenue generating jobs are the unsung heroes of the modern economy. They create the foundation upon which revenue-generating roles can build and succeed. By providing essential support services, maintaining operational efficiency, and fostering innovation, non-revenue generating employees enable their revenue-generating counterparts to focus on driving the company’s growth. Recognizing and investing in these vital roles is crucial for any organization aiming to achieve long-term success and sustainability.







